Modern diesel engines are equipped with an aftertreatment system that plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of the aftertreatment system and understand its components and functions.
What is an Aftertreatment System?
An aftertreatment system is a set of components integrated into a diesel engine’s exhaust system. Its primary purpose is to reduce harmful pollutants emitted by the engine, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO).
Components of an Aftertreatment System
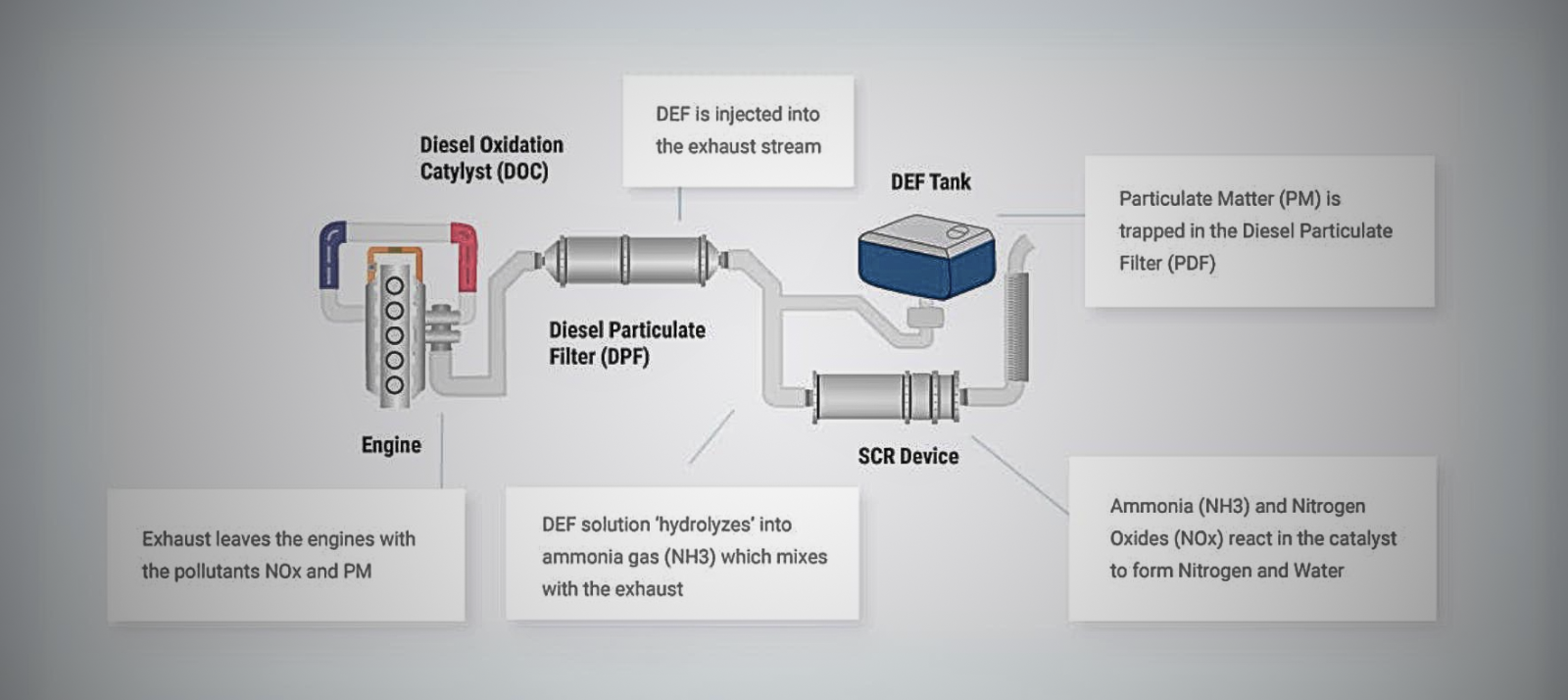
1. Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC): The DOC is the first component in the aftertreatment system. It helps convert harmful carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons into less harmful carbon dioxide and water vapor.
2. Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF): The DPF captures and stores particulate matter, including soot and ash, from the exhaust gases. Over time, the DPF can become clogged and requires periodic regeneration to burn off the accumulated soot and ash.
3. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) System: The SCR system is responsible for reducing nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions. It uses a catalyst and a reducing agent, typically urea-based Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF), to convert NOx into harmless nitrogen and water.
4. Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) Tank: DEF is a solution of urea and deionized water that is injected into the SCR system to facilitate the reduction of NOx emissions. The DEF tank needs to be refilled periodically, depending on the engine’s usage and DEF consumption.
How Does the Aftertreatment System Work?
The aftertreatment system operates in conjunction with the engine control unit (ECU) to monitor and control the engine’s emissions. Here’s a simplified overview of how it works:
1. Exhaust gases from the engine flow into the aftertreatment system.
2. The diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) converts carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons into less harmful compounds.
3. The diesel particulate filter (DPF) captures and stores particulate matter, periodically regenerating to burn off the accumulated soot and ash.
4. The remaining exhaust gases then enter the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system.
5. The SCR system uses a catalyst and diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) to convert nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen and water.
6. The treated exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere, significantly reducing harmful emissions.
Benefits of an Aftertreatment System
The aftertreatment system offers several benefits:
1. Environmental Compliance: By reducing harmful emissions, diesel engines equipped with aftertreatment systems comply with stringent environmental regulations.
2. Improved Air Quality: The aftertreatment system helps in reducing pollutants that contribute to air pollution, thereby improving air quality.
3. Health Benefits: By minimizing the release of harmful pollutants, the aftertreatment system contributes to better public health by reducing respiratory issues and other health problems associated with poor air quality.
4. Fuel Efficiency: Although the aftertreatment system adds some complexity to the engine, it helps optimize fuel efficiency by improving combustion and reducing engine stress.
Maintenance and Care
To ensure the proper functioning of the aftertreatment system, regular maintenance and care are essential:
1. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and guidelines for aftertreatment system components.
2. Use High-Quality Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF): Ensure that you use DEF that meets the required specifications to maintain the effectiveness of the SCR system.
3. Avoid Contaminated DEF: Contaminated DEF can damage the SCR system. Use clean and uncontaminated DEF to prevent any issues.
4. Monitor Warning Lights: Pay attention to any warning lights or error codes related to the aftertreatment system and address them promptly to avoid potential damage.
In conclusion, the aftertreatment system is a vital component of modern diesel engines, helping to reduce harmful emissions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Understanding its components and functions can help diesel engine owners and operators maintain their engines effectively and contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment.
An active aftertreatment system code means that the fault is happening “now.” At Cobra Diesel Performance in Abbotsford, we can diagnose the root cause.